Egypt Excursion 2024
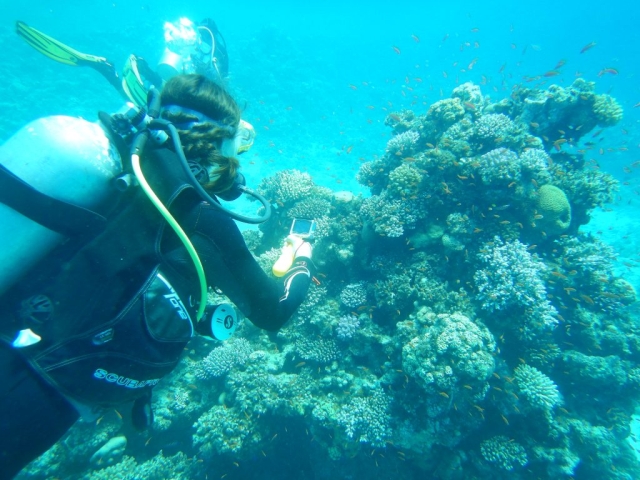
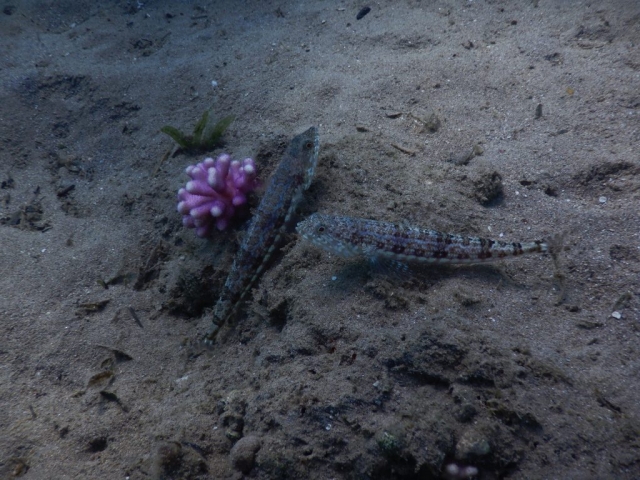
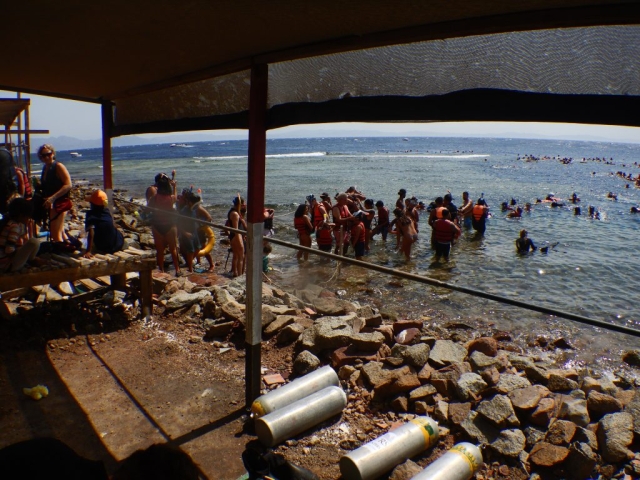
We are just back from this year´s Egypt Excursion! After two days of introductory talks on various aspects of tropical reef diversity and ecology, we explored the amazing biodiversity of the Red Sea for two weeks, spending numerous hours snorkeling and diving. Special thanks to Sinai Divers Backpackers for their great support, all of us had an amazing time in Dahab! Based on videos and photos, we are still adding species to our list, here are some impressions.
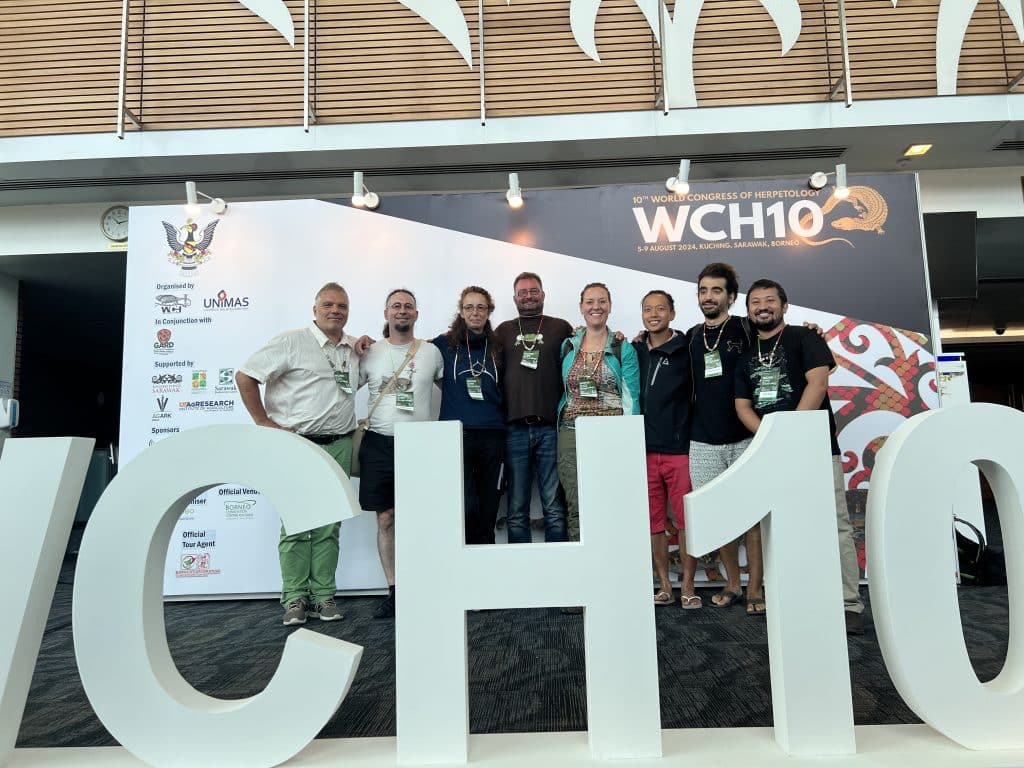
WCH10 Borneo!
Our group is just back from the 10th World Congress of Herpetology, Kuching, Sarawak, Borneo! With 1500+ participants this was one of the largest conferences ever. With 10 participants our group was well represented and our research was communicated in quite many talks and posters, below some impressions from this amazing event.






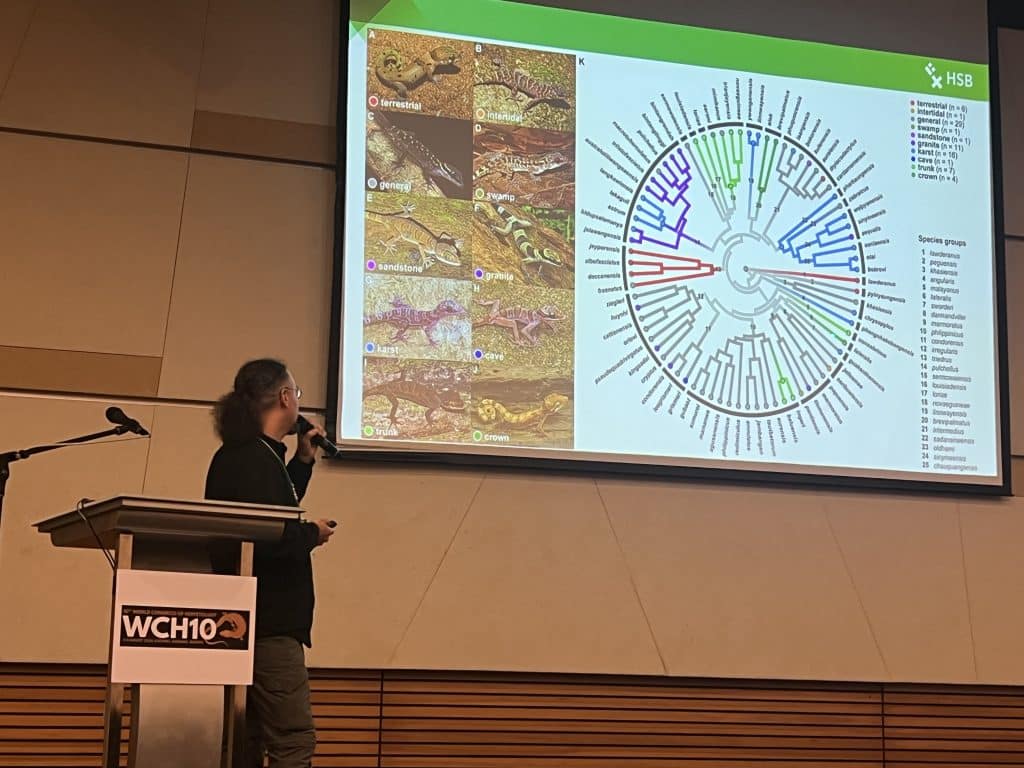













Our contributions in detail:
Auliya, M.: The Global Conservation Status of Varanus Merrem, 1820 – Overview of Threats and Uncertainties in the Assessment of Their Protection Status
In 2003, 58 Varanus species were known to science, today ca. 89 species are known. More than 10 subspecies now have full species rank and new species have been discovered. Currently, 74 species have been evaluated in the IUCN Red List, of which ca. three species require an update due to taxonomic changes, and others likely including new taxa. Among the 74 species, 12 have been assessed in threat categories (CR, EN, VU), two species as Near Threatened (NT), 10 species as Data Deficient (DD), and 50 species evaluated Least Concern (LC). Information on population trends does not necessarily match with Red List categories, e.g., species evaluated LC may have a decreasing population trend. Importantly, in 30 species the population trend is unknown, of which several have been evaluated LC. Year of assessment is crucial to evaluate a species’ current conservation status, in 10 species the year of assessment dates back ≥ 10 years. Analysis of threats indicated in the Red List clearly reveal numerous uncertainties. For almost no species it is possible to indicate the various combinations of threats and the contribution they make to overall declines; accordingly, further research and monitoring is recommended. Various species are utilized for consumption, traditional medicines, hides for the fashion leather industry and the pet trade, with the latter often not indicated in the Red List. Gradually, more space is being given to use and trade as a potential/actual threat, but its assessment as a possible cause of population declines often remains unconsidered. For many Hapturosaurus spp. for example there is a perpetual international demand; information on potential fragmentations of geographically wide-ranging species remain unmentioned, especially when these are well-established lucrative resources. More research is required to eliminate existing uncertainties to establish measures for improved conservation of the Varanidae in the short term.
Baral, S., and D. Rödder: Evaluating wetland policies for the conservation of Mugger Crocodile in Terai-Arc Landscape, Nepal using a spatially explicit population simulation model
Multiple ecosystem services provided by the freshwater ecosystems make them one of the most productive for humans. However, these ecosystems are threatened due to multiple human-induced factors, which have led to the complete or local extinction of many wetland-dependent species and threatening others equivalently. Nepal is no exception to this trend and has lost a significant proportion of healthy wetland ecosystems but only a few policy practices exist for their conservation. In this study, we evaluate the usefulness of these policies to support the conservation of a threatened crocodile the Mugger crocodile in the Terai Arc Landscape of Nepal using a spatially explicit individual-based population model. We define multiple scenarios based on the management recommended by these policies viz. wetland protection in protected areas only, forested areas, government-owned wetlands, and a complete protection of currently identified wetlands. We estimated multiple demographic and dispersal parameters using available literature from multiple species and ran a population simulation model in a freely available program RangeShifter 2.0 for 100 years. We found that the crocodile population persisted for 100 years in all the scenarios. The population at the end of the simulation was significantly higher in the scenario assuming total protection. Maximizing the conservation of wetlands increased the survival of dispersing individuals by creating multiple stepping stones for dispersal and greater availability of habitat patches to hold higher populations. We conclude that the current wetland conservation policies are enough to sustain the population but are not enough to ensure connectivity between the populations. Better protection of available wetland habitats will lead to increased population sizes but might also lead to increased contact with humans. Integrating possible conflict management and means to promote the gene flow of the population in wetland-related policies will promote co-existence in these wetlands.
Bhattacharya, S., M. Auliya and A. Koch: Case Study of Altering Community Perceptions of Monitor Lizards (Varanidae, Varanus spp.) among the Santhal Tribes of Birbhum, West Bengal, India
The “Santhals” are one of the numerous indigenous tribes of India inhabiting several parts of the central and eastern Indian states including West Bengal. Our case study has been conducted in five Santhal villages of the Birbhum district of West Bengal. In spite of the availability of modern food sources and medicines, the tribal communities still significantly utilize and exploit various local wildlife species, especially the Bengal monitor (Varanus bengalensis) and the Yellow monitor (V. flavescens). We explored and documented the utilization patterns, traditional beliefs and taboos related to these species, both of which are nationally protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972. In addition, V. flavescens has been evaluated “Endangered” and V. bengalensis as “Near Threatened” in the IUCN Red List. Moreover, apart from the regular utilization patterns, the Santhals participate in annual hunting festivals, traditionally known as “Bandla Porob”. Semi-structured questionnaire surveys were conducted among the hunters of the tribal communities in five villages. The results provide several direct proofs of local people utilizing monitor lizards for medicines and food. Based on this specific evidence, we designed awareness workshops for the tribal villagers. The main objective of the workshops was to create a widespread perception among the villagers regarding the importance of biodiversity and its sustainable conservation, with a focus on monitor lizards that play a crucial role in their ecosystems.
Chuliver, M., C. Koch and A. Scanferla: Morphology and Ontogeny of Pelvic Girdle and Hind Limb of Thread Snakes (Serpentes: Leptotyphlopidae)
Threadsnakes (Leptotyphlopidae) retain pelvic and hindlimb elements despite of their limblessness. These minute structures can now be studied in detail thanks to novel techniques such as contrast-enhanced micro-CT. In this study, we provide detailed inter- and intraspecific comparisons of the anatomy of the pelvic girdle and hindlimb elements for thirteen species of leptotyphlopids, including ontogenetic and sexually dimorphic variation in Freiberg’s thread snake, Epictia australis. Leptotyphlopids show different degrees of development of their pelvic skeleton, as it might be formed by three elements (ilium, ischium, pubis) with a well-developed femur (Epictia, Leptotyphlops, Trilepida), one rod-like pelvic rudiment of unknown identity attached to a rounded element assigned to the femur (Tricheilostoma), or a single triradiate element (Myriopholis). Intraspecific variation is present in length or robustness of the individual elements, and asymmetries are found in those species having the largest degree of reduction of the elements. In Epictia australis, the ilium is long, posterodorsally directed and curved, its distal end is cartilaginous and can present two different forms. The ischium is posteriorly directed, rod-like, and its distal end is covered by a conical cartilage. The pubis is short, conical and extends anteriorly in opposition to the femur. The femur is the stoutest bone, it exhibits a thin cartilage covering its distal tip, and a rounded protuberance on its proximal region which is directly linked to a keratinized claw. As in other snakes such as boas and pythons, claws are present both in males and females, located anterolaterally to the cloacal region and slightly protruding between scales. This analysis provides new perspectives to discuss the functional and ecological value of pelvic and limb elements in snakes and, therefore, will shed light on relevant topics such as limb loss or vestigial organs as a source of morphological novelties in vertebrates.
Graboski, R., T. M. Cohen, C. Koch, A. M. Bauer and S. Meiri: Systematic and Taxonomic Survey of Israel’s Land Reptile Biodiversity – and a Blind Snake Example
Cryptic species have always posed a challenge for taxonomists. The advent of DNA sequencing has given biologists a new powerful tool for detecting and differentiating morphologically similar species. Yet, taxonomic studies are usually carried out piecemeal, and in many regions, such as most of the Middle East, they are almost nonexistent. We are conducting a rapid genetic survey of the entire reptilian fauna of Israel and examine genetic diversity within currently recognized species to identify potentially cryptic species and describe them. Fossorial snakes belonging to the Scolecophidia commonly show cryptic diversity. To test the status of the Israeli scolecophidian, the Long-nosed worm snake (Myriopholis macrorhyncha), we conducted the most comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of the M. macrorhyncha species complex. Three mitochondrial genes (12S, 16S, and cyt-b) and five nuclear genes (bdnf, cmos, rag1, nt3, and ame) were partially sequenced for 30 specimens belonging to eight species of the group (including three Israeli specimens). Sequences were aligned and a molecular tree was estimated by maximum likelihood (ML). Our tree for the genus shows five well-supported clades: 1) M. longicaudus; 2) “M. macrorhyncha” from Kenya, M. hamulirostris, M. rouxestevae, and M. boueti; 3) M. blandfordii, “M. macrorhyncha” from Ghana, M. adleri, and M. macrorhyncha from Oman and the UAE; 4) “M. macrorhyncha” from Iran and M. algeriensis; and 5) “M. macrorhyncha” from Israel, Jordan, and Turkey. We identify at least two lineages that represent new species and reveal a need for redefining the distributions of many species. Our molecular approach, based on an extensive taxon sampling, show that Myriopholis diversity has been largely underestimated. Our results highlight the importance of molecular data to understand Israeli reptile diversity.
Hofmann, S., D. Rödder, M. Matschiner, R. Masroor, C. B. Baniya, L. J. Borkin, S. Litvintchuk, V. Vershinin, D. Jablonski, L. Podsiadlowski, and J. Schmidt: Endemic amphibian lineages underscore the biogeographic significance of the Hindu Kush Himalaya region
The endemic spiny frogs of the genera Nanorana and Chrysopaa are key elements of the Hindu Kush and Himalayan amphibian fauna and may share a common biogeographic evolution, rendering them valuable tools for reconstructing the paleoenvironmental history of the Himalaya-Tibet-Orogen. However, little is known about the biogeography, systematics, and distribution of these taxa. We provide phylogenomic data and paleoclimatic niche models for Himalayan spiny frogs. The results strengthen support for a trans-Tibet dispersal of ancestral spiny frogs during the Paleogene and highlight the biogeographic importance of the Hindu Kush-Himalaya region.
Kaiser, H., and C. M. Kaiser: Finding Diagnostic Patterns in Morphologically Conservative New Guinea Groundsnakes (Genus Stegonotus): A Closer Look Reveals Undescribed Diversity
Our recent work on the radiation of groundsnakes, genus Stegonotus, has shown that throughout Wallacea and New Guinea the diversity of these snakes has been underestimated. With many populations falling into the category of “nondescript brown snake”, and with a limited availability of molecular data, we have been forced to rely on a rather exacting morphological approach in order to elucidate the taxonomy of the group. By tracing the nomenclature and type localities of species occurring on the island of New Guinea, we found that incorrect species names have previously been applied to two populations from north of the New Guinea Highlands, whose morphology and molecular affinities clearly indicate that they are distinct, unnamed species. In the southwest of New Guinea’s Bird’s Head Peninsula are two populations, whose morphological distinctiveness from Stegonotus ayamaru indicate that they, too, are unnamed species. Lastly, a preliminary survey of Batanta Island revealed the existence of a third species, in addition to S. iridis and S. derooijae, which is distinct in both coloration and scale counts. The presence of three species in the areas under discussion is unsurprising, given that historical collections document the presence of S. diehli, S. poechi, and S. dorsalis in a relatively small area of Madang Province, PNG. It therefore appears that behind the conservative morphology of these snakes is hidden an unrecognized and undocumented resource partitioning ability.
Koch, C: Diversity of Scolecophidian Snakes
Currently 474 scolecophidian snakes are recognized in five families: Anomalepidae, Leptotyphlopidae, Gerrhopilidae, Xenotyphlopidae, and Typhlopidae. In all scolecophidians strong selection associated with a fossorial lifestyle has led to cranial consolidation, miniaturization, and body elongation, resulting in worm-like habits – usually less than 30 cm in total length, and tiny skulls – often just a few millimeters long. Most scolecophidian species look superficially alike, and among all snakes, they are unsurpassed in difficulty of identification due to their low number of diagnostic characters and the difficulties in accurately illustrating and collecting morphological data due to their small sizes. Both, biologically and taxonomically, the scolecophidians are the least studied group of snakes. The presentation gives an insight into external and internal morphological features of Scolecophidia with a special focus on osteological findings. Furthermore, it provides information on the limited data known so far on the biology and some exciting facts about these fascinating reptiles.
Kupfer, A., Q. Martinez and C. Koch: A Brief Introduction to the Diversity of Subterranean Amphibians and Reptiles
Subterranean habitats are usually lightless, hypoxic and hypercapnic inhospitable environments with scarce food resources that lead to strong evolutionary constraints for organisms inhabiting them. Nevertheless, several amphibians and reptiles i.e., caecilian amphibians, fossorial anurans, amphisbaenians, scolecophidian snakes and many more independently evolved a subterranean lifestyle accompanied with diverse adaptations including elongated bodies, robust skulls, stronger forearms, limb reduction, reproductive modes or even a complete loss of the eyesight. However, due to the inaccessibility of the habitat and a lack of sampling methods the knowledge on the biology of burrowing herpetofauna has lacked far behind. The last symposium dedicated to the biology of subterranean herpetofauna i.e, “Quantifying the ecology of burrowing herpetofauna” held at the WCH5 in Stellenbosch, South Africa dates to 2005. Within nearly two decades much information on several aspects of the biology of fossorial amphibians and reptiles has accumulated. The symposium aims to summarise some of these diverse progresses but will also shine a light on the new developments of the research field.
Liz, A. V., D. Rödder, D. V. Gonçalves, G. Velo-Antón, M. J. Paúl, N. Drake, P. Breeze, P. Tarroso, P. Hopcroft, P.-A. Crochet, R. Godinho, S. B. Carvalho and J. C. Brito: Comparative Phylogeography Reveals Ancient Corridors, Refugia and Cradles of Genetic Diversity in Sahara-Sahel Vertebrates
In the Sahara, climatic oscillations between savannah and desert states for at least the last ten Million years left deep imprints on biodiversity patterns. Mountain and coastal areas have been postulated as ecological refugia and diversification centres, at least for the more mesic communities inhabiting the region, and a series of trans-Saharan green corridors connecting the Mediterranean and Afrotropics have also been suggested. However, these biogeographic hypotheses have only been based on a handful of species. Xeric taxa should present different patterns, but even less is known about these. Accordingly, this work seeks to map vertebrate diversity across the arid ecoregions of North Africa (the Sahara and Sahel) in order to consolidate and test biogeographic scenarios for the region since the Miocene. We used >8,500 geo-referenced DNA sequences and > 28,000 occurrence points from 104 vertebrates (reptiles, mammals, amphibians, and birds) to map intra-specific genetic diversity (ISD) and connectivity, and model past species habitat shifts, considering climate, hydrology, vegetation, and substrate information. By analysing the concordance between genetic and ecology-based inferences, we attempted to identify diversity hotspots, refugia and corridors, and compare spatial patterns among mesic and xeric species. For xeric taxa, the northern Sahara, together with the southwestern Sahel, was identified as the main ISD hotspot. Ecological results supported northern Sahara refugia, which extended southwards. For mesic taxa, ISD hotspots covered most Saharan highlands, the Nile Valley, coastal areas, and the Niger Delta. Refugia were mostly concordant with ISD hotspots. Ecological xeric connectivity was overall widespread, while genetic corridors primarily included the Atlantic Sahara, the Nile Valley outskirts, and the eastern Sahel. Mesic corridors included the Atlantic coast and, to a greater extent, the Central Sahara highlands. The patterns recovered by this comprehensive study should help understand the historical biogeography of the largest warm desert on Earth.
O’Shea, M., and H. Kaiser: Introducing the Secretive Serpents of Paradise, the Endemic New Guinea Elapid Genus Toxicocalamus (Elapidae: Hydrophiinae)
Toxicocalamus is a genus of rarely seen, vermivorous, oviparous, hydrophiine elapids, endemic to the island of New Guinea and its satellite islands and archipelagos. A century after George Albert Boulenger named the genus in 1896, Toxicocalamus contained 10 taxa (nine species and one subspecies). However, since 2009, resurgent interest in the genus has elevated this number to 24 species, of which 13 have been examined using molecular data. Toxicocalamus is now the largest, non-marine, alethinophidian snake genus in the Australasian-Melanesian region, and it is set to become even larger as further species will be described in the near future. Yet Toxicocalamus also remains a relatively understudied genus, with dietary preferences and reproductive status largely obtained from post-mortem examination. Toxicocalamus species are almost unique amongst terrestrial Papuan elapids in lacking a temporolabial scale between the penultimate and ultimate supralabials, along with only Pseudonaja. Several members of Toxicocalamus are relatively stout-bodied and quite sizeable (up to 1.0 m in total length in two species), there is also a number of extremely slender “bootlace” species with especially short tails, that may be more fossorial or semi-fossorial in habit. The stouter species exhibit typical colubrid-elapid head scutation; 15-15-15 dorsal scale rows; six supralabials; the cloacal covering consisting of two scales; and paired subcaudals, whereas the “bootlaces” display a great deal of variation. Dorsal scales are arranged in 13-13- 13, 15-15-15, or 17-17-17 rows; subcaudals can be paired or single; the cloacal covering can be formed from one or two scales; the supralabials can number from 4–6, and the species exhibit a diverse array of head scute fusions including fused inteasal + prefrontal; preocular + prefrontal; inteasal + preocular + prefrontal; frontal + supraoculars; supraocular + postocular; and supralabials + temporals, which provide valuable clues that aid in the identification of a specimen in hand.
O’Shea, M., F. Kraus and H. Kaiser: Hidden Diversity and Natural History of the Secretive New Guinean Worm-eating Snakes, Genus Toxicocalamus (Elapidae: Hydrophiinae), Revisited
Toxicocalamus is an elapid genus represented by 526 specimens in thirty collections worldwide. It is a genus of diual but secretive, terrestrial, or fossorial, oviparous, vermivorous snakes, endemic to the island of New Guinea and its satellite islands. These snakes inhabit rainforest, hill and pre-montane forests, or montane grasslands, but one species is especially common in earthworm-rich highland garden systems. Most species are relatively small (< 600 mm in SVL), but two species approach or exceed 1.0 m total length. Many species exhibit distinctive head-scute fusion arrangements that greatly aid in their identification. The genus was erected in 1896 by George Albert Boulenger based on T. longissimus from Muyua (Woodlark) Island, a satellite of New Guinea off the southeast coast of New Guinea. During the remainder of the 19th Century additional species were described, both in Toxicocalamus but also in three other genera (Apistocalamus, Pseudapistocalamus, Ultrocalamus) that were later reduced to subgenera within Toxicocalamus. By the end of the 1960s, Toxicocalamus comprised nine species, and this number remained constant for forty years until a new generation of herpetologists started to investigate the genus. Since 2009 a further twelve species have been described and three have been resurrected from synonymy, bringing the current total to 24 species, making Toxicocalamus the most diverse terrestrial alethinophidian snake genus east of the Wallace Line and descriptions of further new species are currently in preparation.
Parmar, D. S., and H. Kaiser: Sparks among the snakes? A potential genetic explanation for unusual color morphs in Daboia russelii (Shaw & Nodde, 1797) and Lycodon aulicus (Linnaeus, 1758) from India
Along with the well-documented color polymorphisms of various snakes bred in the pet trade, more and more reports of color aberrations in snakes encountered in the wild are being published. This is likely a consequence of the increased activities of snake rescue teams around the globe and the resultant higher level of snake awareness among local human populations. We found unusual color morphs in two vipers, Daboia russelii, and a wolfsnake, Lycodon aulicus, in India. These snakes display a strongly abnormal coloration, with near-leucistic and unpatterned vipers and a nearly unpatterned wolfsnake. Yet each of these snakes possesses striking vertebral lines. The uniformly brown L. aulicus has a normal neck band but the expected transverse banding pattern is missing. The coloration of the vertebral scale row and its two adjacent scales creates a longitudinal pattern of a dark brown vertebral line framed in a cream color, beginning 11 scales beyond the parietals and extending two thirds the body length. In contrast, the line pattern in the vipers begins at the neck and consists of three un- or lightly pigmented scales along the vertebral line, framed by a single row of dark scales on either side and extending more faintly onto the posterior part of the body. While the primarily white viper from Gujarat retains the dark lateral rings that typically offset different shades of brown in normal phenotypes, the body of the subadult from Goa is a patternless light brown. The patterning is strongly reminiscent of a genetic modification in the pathway controlling chromatophore development that has been called spark/spark in ball pythons (Python regius). Detailed genetic studies of this phenomenon would be ideal, but the uniqueness of these color aberrations in these two species makes such work impractical – but it reveals nature as a sometimes-eccentric painter of lines.
Reilly, S. B., B. R. Karin, U. Arifin, H. Kaiser, A. L. Stubbs, E. Arida, A. Hamidy, D. T. Iskandar and J. A. McGuire: Phylogenomics of Lesser Sunda Emerald Tree Skinks (Lamprolepis smaragdina) Uncovers a Broad Range Expansion Followed by Low Gene Flow
The Emerald Tree Skink, Lamprolepis smaragdina, is an arboreal lizard that is well adapted to over-water dispersal and is found throughout Wallacea and the western Pacific islands. These lizards are found on every major island in the Lesser Sundas where they exhibit one or more of three distinct color patterns: a green morph, a brown morph, and a half-green half-brown morph. Given this species’ propensity to successfully disperse from island to island, we expected to find moderate levels of gene flow and low genetic divergence between Lesser Sunda island populations. We used both mitochondrial (1426 bp for 174 lizards) and exoncapture (1411 sequence loci for 104 lizards) datasets to reconstruct phylogenetic relationships and estimate divergence times and levels of migration for L. smaragdina populations across 12 Lesser Sunda islands. The results support a scenario where the Lesser Sundas assemblage diverged from the Peleng Island (off eastern Sulawesi) population ~1.5 Ma with subsequent dispersal events within the Lesser Sundas occurring between 1–0.4 Ma. Biogeographical model testing supports a scenario where many dispersal events occur parallel to or against major longterm oceanic currents of the “Indonesian Throughflow”. While some of the mito-nuclear discordances indicate secondary dispersal events have occurred between established populations, genomic estimates of migration show near total genetic isolation of all populations. This implies that either population sizes are too large to detect the genes of more recent migration events, or that recent migrants are unable to successfully reproduce with the established population.
Riedel, J., K. Eisele, Y. Ecker, T. Higham, J. Wu, Q. H. Do, T. Q. Nguyen, C. G. Meneses, R. M. Brown, L. L. Grismer, T. Ziegler, A. P. Russell, and D. Rödder: Evolution of incipient toepads in a radiation of ecologically diverse geckos
Adhesive toepads have evolved repeatedly in a variety of clades to promote attachment to inclined surfaces in climbing species. Among amniotes, geckos are the most thoroughly studied with regard to their adhesive toepads. Even so, the evolutionary origin of these complex structures is still elusive, this being partially due to the scarcity of studies on species with incipiently developed toepad morphologies. One suggested model for the presence of incipient toepads are the bent-toed Geckos (Genus Cyrtodactylus), an ecologically diverse radiation, the climbing members of which possess enlarged subdigital scales. It is known that a few such species carry spatulated setae as microstructures on these scales. Given this, we explore the evolution of incipient toepad morphology in Cyrtodactylus species from different microhabitats (ecotypes) in relation to habitat use (terrestrial, arboreal, rock-dwelling and generalists) to unravel how and under which ecological circumstances adhesive toepads evolved. We measured size-corrected subdigital scale area, examined subdigital scale shape using 2D geometric morphometrics, and subdigital microstructures using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). We reconstructed the evolution of these traits and tested whether species occupying different microhabitats differed in their subdigital scale morphology. We found that both arboreal and rock-dwelling species had relatively larger subdigital scale areas, but partly differed in scale shape. Microstructures also differed among ecotypes with spatulated setae being more prevalent in climbing species.
Riedel, J., L. L. Grismer, T. Higham, J. Wu, Q. H. Do, T. Q. Nguyen, C. G. Meneses, R. M. Brown, P. D. Campbell, T. Ziegler, A. P. Russell and D. Rödder: Ecomorphology of the Locomotor Apparatus in the Genus Cyrtodactylus (Gekkota, Squamata)
Adaptive radiations garner considerable interest from evolutionary biologists. Lizard radiations diversifying along structural niche space often exhibit distinct changes in body and limb proportions. One prediction is that terrestrial species inhabiting open habitats will have relatively longer hindlimbs, associated with faster running speeds, while scansorial species will have relatively shorter limbs to keep the centre of mass closer to the substratum. Alternatively, terrestrial species in densely vegetated habitats could benefit from relatively shorter limbs to prevent entanglement with more frequently encountered obstacles, whereas scansorial species could benefit from longer limbs promoting greater limb spans and static stability. Cyrtodactylus, an ecologically diverse gekkonid genus, includes numerous specialists with narrow structural niches, but the degree of morphological diversification exhibited by these specialists is largely unknown. We investigated associations between locomotor morphology and structural microhabitat use in Cyrtodactylus to test if either of the opposing predictions can be corroborated for this radiation. We measured body length and relative limb dimensions of 87 species, covering multiple independent transitions among structural microhabitat preferences. Using these data, we reconstructed the phylomorphospace and tested for associations between structural microhabitat niche and limb morphology. We found strong separation between structural niche groups in accordance with the second hypothesis, although overlap is evident among functionally related niches such as those of granite and karst specialists.
Rödder, D., J. Secondi, J. Altenhofen and G. Vimercati; The Relative Influence of Habitat Availability, Landscape Configuration and Spatial Sorting on Population Expansion in Xenopus laevis: A Simulation Test
Population expansion into new areas is a common phenomenon driven by changes in ecological conditions. It also increasingly results from human-assisted introduction of propagules into novel environments, which leads species to spread into areas where they did not evolve and cause various ecological and socio-economic impacts. Spatial sorting (the enhanced dispersal capacity in expanding populations over time) and landscape configuration are two factors that largely influence the way organisms move across a landscape and reach locations to complete their life cycle. While both factors have been frequently studied independently, their relative influence to modulate the spread rate of expanding populations has been significantly unexplored. We simulated the spread of an invasive amphibian, Xenopus laevis, in various landscapes of its colonized ranges and surroundings in western France. By using the software UNICOR, we ran colonization simulations on 30 x 30 km cells of an experimentally parameterized resistance layer at three settings of spatial sorting. Results show that habitat availability (ponds density) and spatial sorting positively affected the rate of population expansion in the cells and interacted: higher spatial sorting and pond density increased the invaded area, number of colonized ponds and maximal traveled distance per time unit. In contrast, none of the four landscape configuration metrics improved the models, suggesting that this factor has limited influence on population expansion. The effect of spatial sorting on population spread was enhanced by pond density but not by landscape configuration. These results may partly reflect the high density of ponds and the relative contribution of landscape configuration may be reevaluated in different landscape types. Nevertheless, these highlight the importance to consider jointly habitat availability and spatial sorting in predictive modeling of the spread process in expanding populations, such as those that characterize many alien species.
Tan, W. C., V. Vitalis, J. Sikuim, D. Rödder, M.-O. Rödel and S. Asad: High Freshwater Turtle Occupancy in a Sustainably Managed Tropical Forest, Borneo
Despite suffering dramatic declines due to habitat loss and overexploitation, tortoises and freshwater turtles, particularly those in Southeast Asia remain largely understudied. This region is not only a diversity hotspot, but also the centre of an international turtle trade and increasing anthropogenic pressures. In the face of these threats, the utility of sustainable forest management for the conservation of threatened freshwater turtle populations is unknown. This study examines the impact of Reduced Impact Logging, a sustainable forestry method, on two freshwater turtle species. We examined the detectability and habitat relationships of a threatened hard-shelled turtle, Notochelys platynota and a non-threatened soft-shelled turtle, Dogania subplana within a commercial forest reserve in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. Using single-species occupancy models, we identified covariates associated with the detection and occupancy probabilities of the species across a post-harvest recovery gradient (1–21 years since logging). Results for D. subplana were inconclusive. In contrast, we found a significant negative association between monthly rainfall and N. platynota detectability. The occupancy probability of N. platynota was positively associated with greater distance from logging roads and higher stream flow accumulation. Occupancy probability for N. platynota and D. subplana was relatively high throughout the reserve. These results, suggest that forests managed sustainably, i.e. using RIL methods, could serve as invaluable conservation areas for imperiled freshwater turtle species in the region.
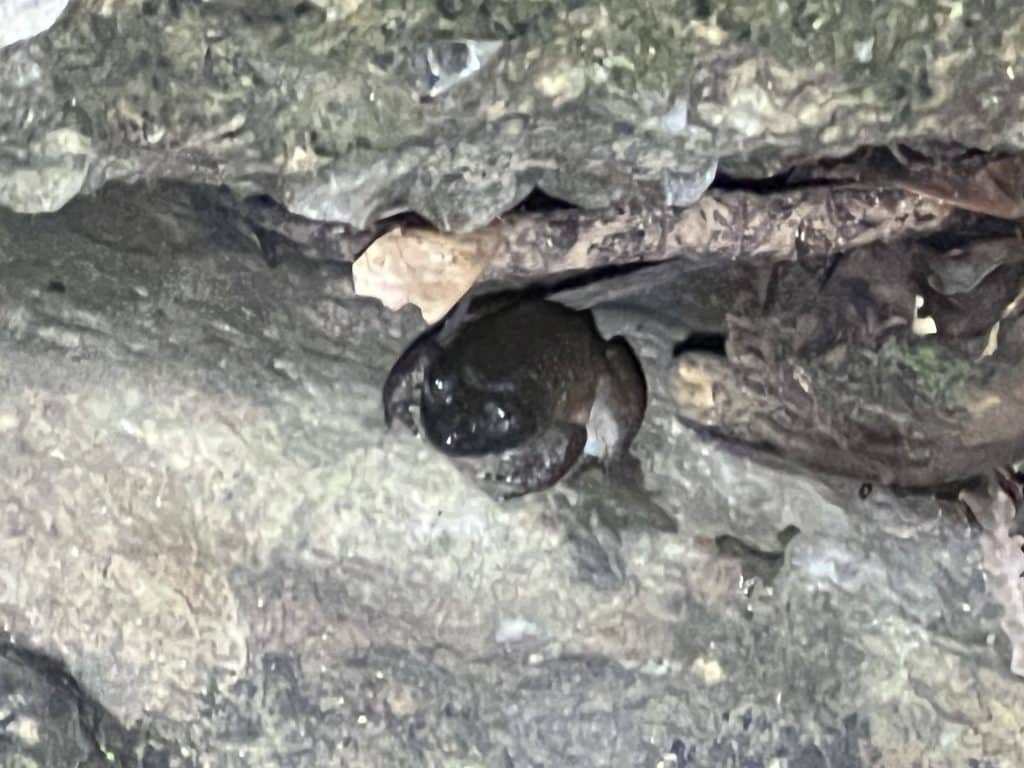
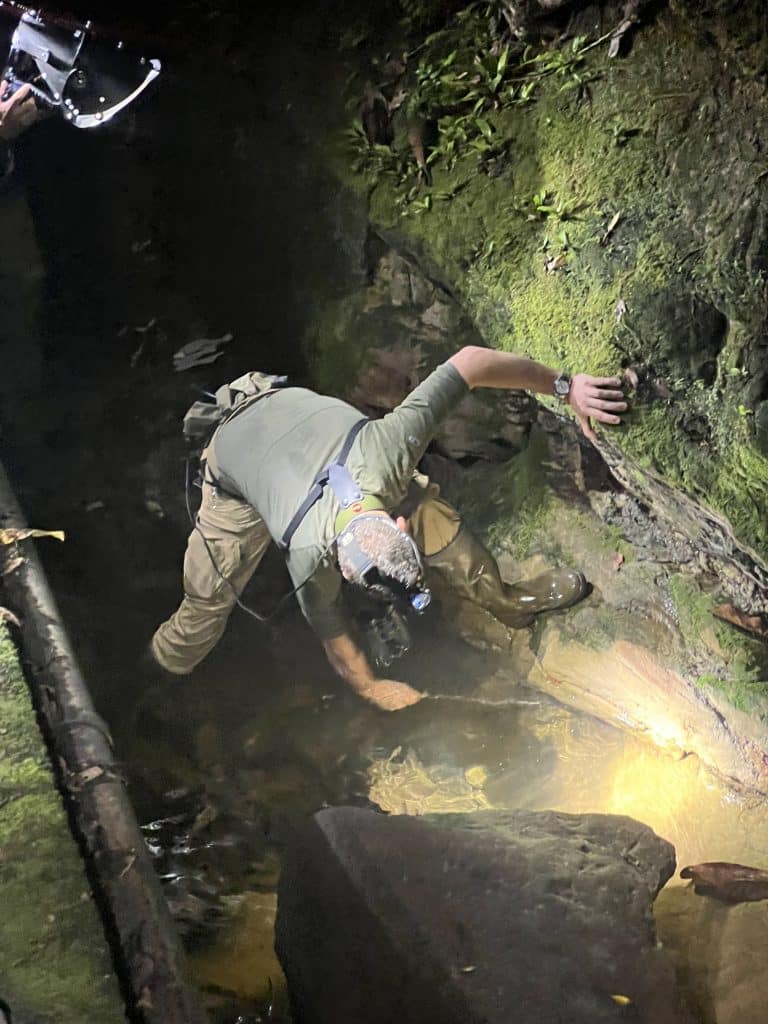
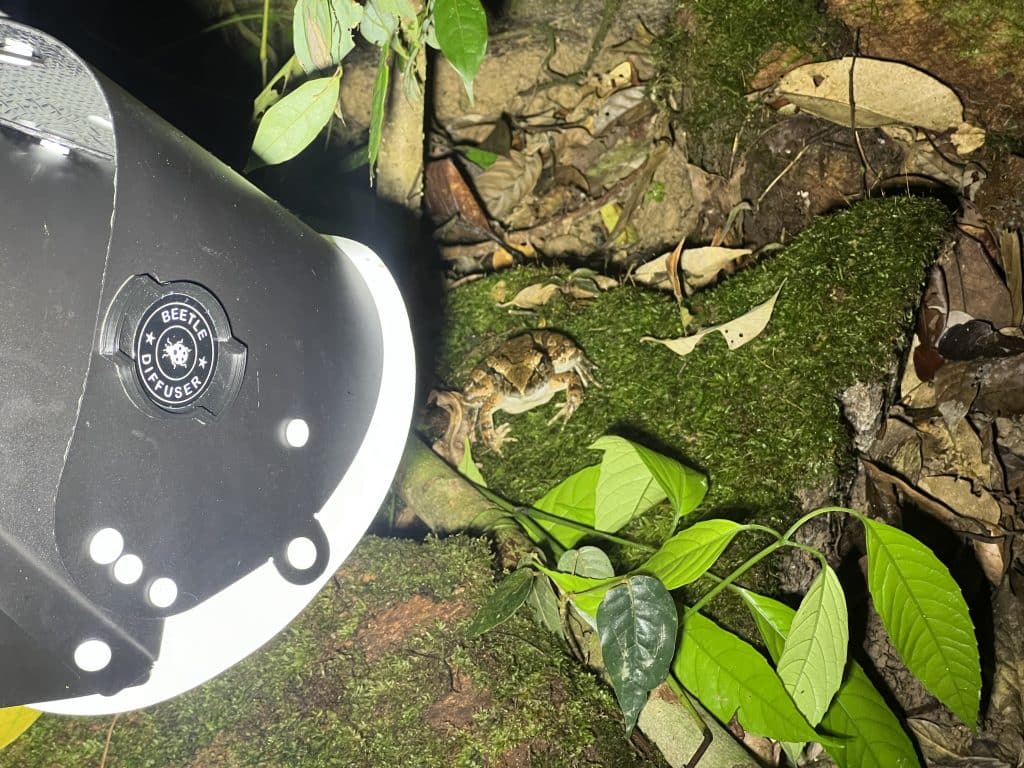
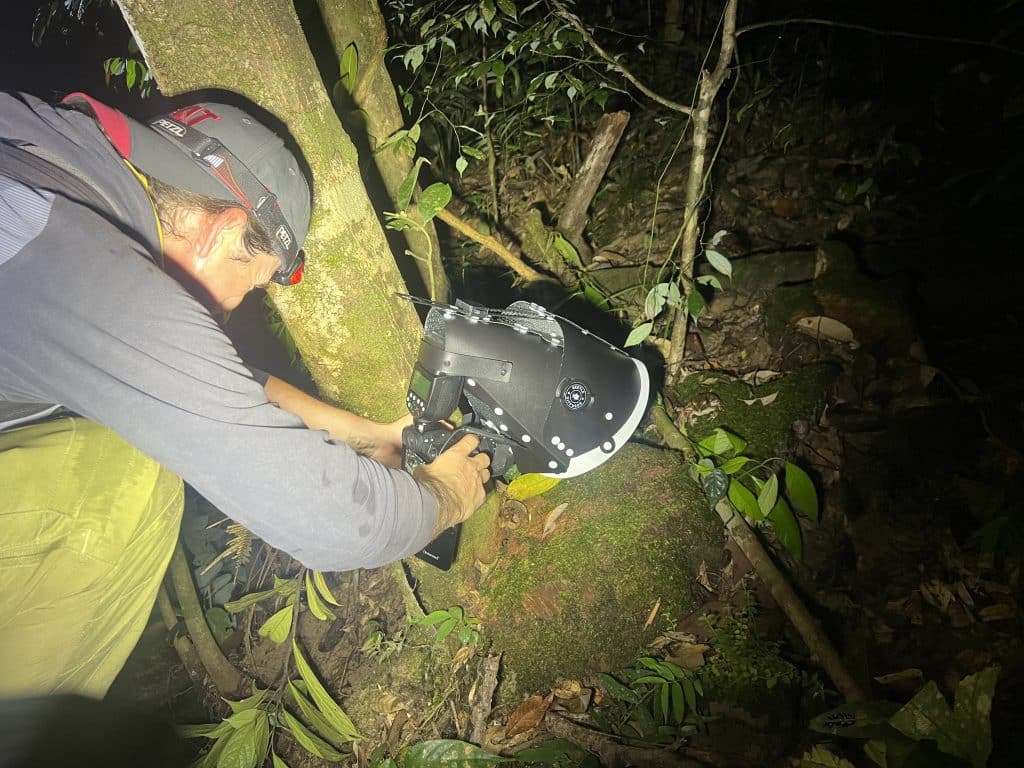



























PhD defense of Wei Cheng Tan
Wei Cheng Tan has just very successfully defended his PhD thesis!
“Effects of habitat fragmentation on herpetofauna in Southeast Asia: From broad-scale responses to fine-scale responses in an ever-changing anthropogenic landscape“
Abstract
Habitat loss and fragmentation are undoubtedly significant drivers of biodiversity loss worldwide, with Southeast Asia being a hotspot of biodiversity and facing numerous anthropogenic pressures. However, the impacts of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity are still not fully understood, and further research is required to determine the responses of different taxa to this threat. Reptiles and amphibians (herpetofauna), in particular, are among the most threatened groups globally, with Southeast Asia being home to a high diversity of species and facing imminent threats from habitat loss and fragmentation. By combining bibliographic analyses and macroecological methods, this thesis aims to contribute to the knowledge on the current global state of habitat fragmentation research in herpetofauna and the broad and fine-scale responses of Southeast Asian reptiles to various forms of habitat fragmentation.
Chapter 1: This chapter introduces the concepts of habitat fragmentation and its effects on biodiversity. It accentuates the importance of Southeast Asia for habitat fragmentation research due to its complex geological history, high species richness, and rapid habitat loss. It also describes the plight of the Southeast Asian herpetofauna, focusing on their vulnerability to habitat loss and fragmentation in freshwater environments. Lastly, the chapter gives a brief overview of the methodologies and approaches used throughout this thesis.
Chapter 2: Recent decades have seen a surge of funding, published papers, and citations in the field as threats to biodiversity continue to rise. However, how research directions and agendas are evolving in this field remains poorly understood. This chapter presents a global review of past and current state of research on habitat fragmentation for reptiles and amphibians. Here, I systematically reviewed published literatures on habitat fragmentation effects on reptiles and amphibians from 1990 to 2020, with the aim of identifying geographical and taxonomical trends on the various forms of habitat fragmentation, and the sampling methods and response variables commonly employed to identify them. The study reveals several patterns and biases in research efforts, such as the concentration of studies in wealthy and English-speaking countries, and the under-representation of certain regions (e.g. Africa and Southeast Asia) and taxa (e.g. caecilians, fossorial reptiles). It specifically calls for increased attention to these taxa in Southeast Asia, which have received less scientific scrutiny compared to other regions of the world. Moreover, there is a shift in research agendas toward studies utilizing technological advancements including genetic and spatial data analyses. These findings suggest important associations between sampling methods and prevalent response variables but not with the forms of habitat fragmentation. This review suggests the need for more studies on genetic and spatial patterns, with emphasis on underrepresented reptile and amphibian taxa. This chapter sets the context for the subsequent chapters by highlighting the existing gaps in the field.
Chapter 3: This chapter uses species distribution models to investigate the broad-scale responses of threatened semi-aquatic or freshwater reptiles to current and future climatic and anthropogenic conditions. More specifically, it examines the habitat suitability of endangered freshwater crocodiles and turtles and assesses the effectiveness of existing protected areas in conserving these species across Southeast and South Asia (in the Indomalayan realm). Species distribution models are highly successful in predicting potentially suitable habitats of a species based on their environmental niche and presence records. The results suggest that protected areas may be insufficient in the face of current anthropogenic pressures and future climate change. The chapter emphasizes the importance of considering both climatic and non-climatic factors in species distribution models. The results of this chapter are essential for conservation planning and management, as they provide insights into important areas and reserves that should be prioritized.
Chapter 4: This chapter zooms in from a broad-scale to fine-scale view of species response to habitat change, focusing on the effect of logging, which affects more than half of the remaining tropical forests in Southeast Asia. Logging has direct and indirect impacts on freshwater turtle habitats, such as altering stream hydrology and increasing sedimentation. In this chapter, I examine the fine-scale responses of two freshwater turtle species to Reduced Impact Logging, a sustainable forestry method, in Deramakot reserve in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. I use occupancy models to estimate the probability of species detectability and habitat associations across a post-harvest recovery gradient (1 –21 years since logging), using presence and absence data. Results for the non-threatened soft-shelled turtle, Dogania subplana are inconclusive. However, the study reveals a significant negative association between monthly rainfall and the detection of the threatened hard-shelled turtle, Notochelys platynota. The occupancy probability of N. platynota is positively associated with greater distance from logging roads. Nevertheless, both species appear to be relatively common throughout the reserve. The chapter suggests that forests managed sustainably, i.e. using Reduced Impact Logging could serve as conservation areas for imperiled freshwater turtle species in the region.
Lastly, chapter 5 summarizes the results of this thesis and its implications and contributions to the field. It also considers the limitations of the approaches and methodologies used. Overall, this thesis emphasizes the urgent need for more research on the effects of habitat fragmentation on herpetofauna in Southeast Asia and the importance of incorporating both broad and fine-scale data. This work is a significant step towards providing easily reproducible studies to be used as a baseline to ensure the long-term survival of these vulnerable species in Southeast Asia.
These papers are already published and included in the thesis:
Harrer, S., P. Ginal, W. C. Tan, J. W. Binaday, A. C. Diesmos, R. Manalo, T. Ziegler, and D. Rödder. 2024. Disappearing archosaurs – an assessment of established protected areas in the Philippines to save the Critically Endangered, endemic Philippine Crocodile (Crocodylus mindorensis). Salamandra 60: 29-41. (PDF)
Mobaraki, A., M. Erfani, E. Abtin, J. C. Brito, W. C. Tan, T. Ziegler, and D. Rödder. 2023. Last chance to see? Iran and India as strongholds for the Marsh crocodile (Crocodylus palustris). Salamandra 59: 327–335. (PDF)
Tan, W. C., A. Herrel, and D. Rödder. 2023. A global analysis of habitat fragmentation research in reptiles and amphibians: What have we done so far? Biodiversity and Conservation 32: 439–468. (PDF)
Tan, W. C., P. Ginal, A. G. J. Rhodin, J. B. Iverson, and D. Rödder. 2022. A present and future assessment of the effectiveness of existing reserves in preserving three critically endangered freshwater turtles in Southeast Asia and South Asia. Frontiers of Biogeography 2021, 14.1, e50928. (PDF)



PhD defense of Philipp Ginal
Philipp Ginal has just very successfully defended his PhD thesis!
“Invasion biology of amphibians and reptiles: From observations to predictive spatial models”
His thesis entitled “Invasion biology of amphibians and reptiles: From observations to predictive spatial models” comprises six publications. Overall, his thesis is broadly folded, and comprises several target species across different taxonomic groups (i.e., anurans, urodeles, squamates), scales (i.e., local, regional, macro-ecological landscapes), and methodological approaches (i.e., population size estimation, connectivity modeling, correlative and mechanistic species distribution modeling, mechanistic quantification of activity time budgets). The focus of my thesis relies on the methodological approaches and therefore, the red line here starts with relatively simple models and ends with a novel, complex mechanistic approach.
Furthermore, three publications consider the African Clawed Frog, Xenopus laevis (Daudin, 1802), which is among the most invasive amphibian species in the world.
Two further publications focus on the Oriental Garden Lizard, Calotes versicolor (Daudin, 1802) complex, a wide-spread but neglected invader with potential negative impacts, and the Italian Cave Salamander, Speleomantes italicus (Dunn, 1923), which is non-native but locally very restricted with no known negative impacts yet. Another publication considers the invasive fungal disease Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans Martel et al. 2013 (Bsal), which has substantial negative impacts on macro-ecological scales, and one of its host species, the European Fire Salamander, Salamandra salamandra (Linnaeus, 1758).
These papers are already published and included in the thesis:
Ginal, P., N. Kruger, C. Wagener, L. Araspin, M. Mokhatla, J. Secondi, A. Herrel, J. Measey, and D. Rödder. 2023. More time for aliens? Performance shifts lead to increased activity time budgets propelling invasion success. Biological Invasions 25: 267–283. (PDF)
Ginal, P., W. C. Tan, and D. Rödder. 2022. Invasive risk assessment and expansion of the realized niche of the Calotes versicolor species complex (Daudin, 1802). Frontiers of Biogeography 14.3, e54299. (PDF)
Ginal, P., M. Mokhatla, N. Kruger, J. Secondi, A. Herrel, J. Measey, and D. Rödder. 2021. Ecophysiological models for global invaders: Is Europe a big playground for the African clawed frog? Journal of Experimental Zoology – Part A: Ecological and Integrative Physiology 2020: 158-172. (PDF)
Ginal, P. C.-H. Loske, T. Hörren and D. Rödder. 2021. Cave salamanders (Speleomantes spp.) in Germany: tentative species identification, estimation of population size and first insights into an introduced salamander. Herpetology Notes 14: 815-822. (PDF)
Ginal, P., F. D. Moreira, R. Marques, R. Rebelo, and D. Rödder. 2021. Predicting terrestrial dispersal corridors of the invasive African clawed frog Xenopus laevis in Portugal. NeoBiota 64: 103–118. (PDF)
André Vincente Liz: PhD defense
Comparative phylogeograpy of the Sahara – Sahel: a spatiotemporal approach to biodiversity dynamics in the largest warm desert on erth
Our PhD Student André Vincente Liz just successfully defended his PhD thesis, congratulations! A full recording of the defense is provided by the University of Porto.
Abstract
The Sahara-Sahel environments are home to rather endemic desert biotas highly adapted to the region’s aridity constraints and the dry/humid climatic cycles that took place throughout the Plio-Pleistocene. Species’ contemporary patterns harbour a crucial potential to understand the impacts of these steep fluctuations on the desert’s landscape, as well as to develop integrative conservation agendas that help preserving a highly vulnerable local wildlife. Yet, this baseline biological knowledge has been traditionally lacking for the region. With the advent of molecular phylogeography at the end of the 20th century, biodiversity studies in the Sahara-Sahel have started unravelling novel aspects of its intricate natural history, primarily how palaeoclimatic and subsequent land-cover shifts have shaped the distribution and genetic structure and diversity of local species by triggering different eco-evolutionary processes. Core biogeographic and evolutionary hypotheses have been posed, including population divergence in allopatry, which often led to speciation, dispersal and colonisation of new environments, including trans-Saharan migrations across the desert, or events of secondary contact. Notwithstanding the remarkable recent advances in regional research, biodiversity patterns in some of the most unique features within the region’s eco-physiographic diversity remain virtually unknown. Besides, the phylogeographic scenarios that have been proposed lack corroboration under a common framework.
Aiming to provide the first comprehensive picture of biodiversity patterns in the Sahara-Sahel, this thesis builds upon a comparative phylogeography framework that seeks to verify and expand the major biogeographic and evolutionary questions posed for the region. For this purpose, I assessed all publicly available DNA data for Sahara-Sahel vertebrates (i.e., >1,000 species) and selected the most relevant taxa based on data availability and species’ distribution within the study area. I tested phylogeographic scenarios through the integration of different molecular and eco-geographic analyses, including phylogenetics, phylogeography, population genetics, species distribution modelling (SDM), and geostatistics. These analyses allowed inferring the location of ecological refugia, dispersal corridors, and hotspots of intra-specific diversity for regional species according to their habitat requirements, i.e. those more- (xeric) or less (mesic) adapted taxa to the desert’s extreme aridity. Considering that the advent of arid conditions in North Africa triggered the diversification of the most xeric taxa, examining the phylogenetic ages of these species allowed estimating the chronology of the Sahara for the first time from a biological point of view. During the development of this thesis, I also generated new biodiversity data that allowed examining phylogeographic hypotheses in poorly known regions of the Sahara-Sahel, which yet constitute key elements to understand the region’s natural history. Specifically, I (1) addressed the role of Central Sahara highlands in historical biodiversity dynamics, and (2) examined biodiversity patterns throughout the hyper-arid Sahara.
Notably, the phylogenetic insights brought by xeric taxa suggest that the onset of aridification in North Africa occurred in the Mid Miocene, contrasting remarkably with geological and climatological findings. The age of the Sahara is still a controversial topic; evidence for this is that new studies keep reporting contrasting estimates: from 7 up to 11 Myr. This thesis provides the first comprehensive chronology for the impact of regional aridification on Saharan wildlife. Beyond vertebrates, this work also looked at the age of the remaining taxonomic groups for which molecular data was available (i.e., scorpions), given the low number of species that occupy the desert’s extreme environments. This analysis highlighted the need for systematic assessments on Saharan xeric arthropods, such as beetles, spiders or grasshoppers, which present profound knowledge shortfalls despite being major elements within the region’s biological diversity.
Concerning the lack of phylogeographic knowledge for some of the least known regions of the Sahara-Sahel, two studies were conducted. In the first one, I assessed whether the mountains of Central Sahara acted as historical ecological refugia and diversification hotspots for mesic taxa, while also aided in trans-Saharan faunal translocations during humid desert stages. Insights come from the phylogeographic assessment of Acanthodactylus boskianus, a species complex inhabiting mesic environments and distributed at both sides of the desert and in scattered populations throughout the Central Sahara highlands. Results revealed that mountains in Southern Algeria (i.e., Tassili N’Ajjer, Ahaggar), South-western Libya (i.e., Fezzan, Akakus), Niger (i.e., Aïr), and Northern Chad (i.e. Tibesti) harbour historical climatic stability that favoured the local persistence of A. boskianus. Besides, the few genetic samples available from the region recovered high local lineage diversity, with reports of old and mountain endemic clades. Lack of genetic differentiation between some Mediterranean, Central Saharan, and Sahelian populations suggest the existence of recent gene flow between both sides of the desert, which could be explained through the intermittent ecological suitability here observed across interconnected Central Sahara mountainous refugia. In the second study, I analysed the genetic structure and diversity of species inhabiting the most arid environments of the Sahara, where knowledge on biodiversity patterns was almost inexistent. For this purpose, I conducted a phylogeographic assessment of the Acanthodactylus scutellatus complex, which embeds six currently recognised species that possibly comprise the most widespread vertebrates across hyper-arid Saharan habitats. Results recovered surprisingly high levels of intra-specific diversity, including several previously unknown sympatric or parapatric lineages that exhibit both nuclear and mitochondrial differentiation, suggesting species status. These findings evidence that biodiversity estimates for xeric Saharan habitats are likely neglecting a notable amount of undescribed diversity, which seemingly originated in allopatry due to the steep habitat fluctuations that took place throughout the Plio-Pleistocene. Interestingly, the origin of some of these lineages dates back to the Miocene, coinciding with the onset of dry/humid fluctuations in North Africa. Some environments of the northern Sahara, such as the Algerian ergs (i.e., sand-dune fields), were found to be particularly rich in terms of intra-specific diversity. A contrasting pattern was found across southern Sahara latitudes and the Sahel, where the lack of genetic differentiation between distant populations suggested that population dispersal at this latitude was common. The assessment of individual lineage genetic imprints allowed delimiting potential areas of refugia within these desert corridors, however, fine-scale research is needed to clarify whether they correspond to specific landscape features such as palaeolakes, ergs or mountain outskirts.
The primary component of this thesis was the comparative phylogeography assessment, which I conducted after setting the biological chronology of the desert, generating additional data, and refining key phylogeographic hypotheses. This meta-analysis was conducted through the integration of molecular and ecological components for 107 selected desert taxa, including reptiles, mammals, amphibians, and scorpions. During this process, roughly 8,500 DNA sequences were analysed, most of them corresponding to published data retrieved from GenBank and some newly produced to fill key taxonomic and geographic gaps. The analyses of DNA information allowed estimating areas of high genetic diversity and connectivity for each individual species, as well as for the mesic and xeric communities. The molecular component was integrated with an SDM approach, which expanded the methodological framework traditionally applied to biodiversity assessments in the deserts of North Africa. As such, I incorporated for the first time historical hydrological and vegetation data into the SDM pipeline, thus considering previously overlooked ecological dimensions which likely played a major role in historical species responses to dry/wet fluctuations. The historical shifts in species’ range were modelled for the selected 107 taxa using over 28,000 observation records. Results allowed verifying the major biogeographic and evolutionary questions previously proposed for the region. Patterns of intra-specific diversity confirm that the isolated mountains of Central Sahara are important centres of diversity, several of which still lack baseline biodiversity knowledge, with clear examples in Chad (i.e., Tibesti, Ennedi) and Sudan (i.e., Jabal Marrah). High diversity was also found across the northern Sahara for xeric taxa, suggesting that this region harbours a crucial role in the evolution and persistence of truly-desert species, despite local biodiversity patterns being also poorly known. Refugia inferences corroborate the importance of the Atlantic region for most of the species, as well as northern Sahara areas for xeric taxa and mountains for mesic taxa. Additionally, patterns of genetic and ecological connectivity confirm that corridors across Central Sahara highlands played a major role in trans-Saharan dispersals, which can be comparable to that of the Nile Valley and the Atlantic Coast.
This thesis provides integrative knowledge that can be immediately applied to biodiversity conservation agendas in the deserts of North Africa, as well as to the study of biodiversity in deserts and arid regions. In addition, insights on species’ genome and habitat imprints expand our understanding of the natural history of the region, with implications for the evolution and migration of both the desert’s endemic biotas and the early humans that peopled the Sahara and dispersed out of Africa at the end of the Quaternary. Besides, this thesis opened new biogeographic and evolutionary questions that would require additional research efforts, as well as pinpointed areas of dramatic biodiversity shortfalls that should be targeted in future studies.
Parts of his thesis are already published:
Liz, A. V., D. Rödder, D. V. Gonçalves, G. Velo-Antón, M. M. Fonseca, P. Geniez, P.-A. Crochet, and J. C. Brito. 2023. Overlooked species diversity in the hyper-arid Sahara Desert unveiled by dryland-adapted lizards. Journal of Biogeography 50: 101–115. (PDF)
Liz, A. V., D. V. Gonçalves, G. Velo-Antón, J. C. Brito, P.-A. Crochet and Rödder, D. 2022. Adapt biodiversity targets to climate change. Science 376: 589-590. (PDF)
Liz, A. V., D. Rödder, D. V. Gonçalves, G. Velo-Antón, M. M. Fonseca, P. Geniez, P.-A. Crochet, and J. C. Brito. 2021. The role of Sahara highlands in the diversification and desert colonisation of the Bosc’s fringe-toed lizard. Journal of Biogeography 48: 2891–2906.
Egypt Excursion 2023
We are just back from this year´s trip to Egypt! My students and I had a great two weeks of lectures and hands-on experience in a tropical coral reef. Spending many hours on snorkeling and diving we are still determining marine life. The species list contains already over 200 taxa and the numbers are still growing. Here are some impressions from the excursion.
Assessment of the threat status of reptile species from Vietnam – Implementation of the One Plan Approach to Conservation
Just published:
Subsequent to a recently published study in Nature Conservation highlighting the gaps in the protection of Vietnam´s amphibians, Thomas Ziegler and his international cooperation team now present another threat analysis, this time dealing with a detailed assessment of Vietnam’s reptile fauna to uncover gaps in conservation.
Globally, reptiles are considered a group of special conservation concern, as they play an important role in almost all ecosystems and often have relatively small distribution ranges, making them especially vulnerable to anthropogenic threats.
As Vietnam’s herpetofauna is among the richest in the world and particularly threatened due to habitat loss and overharvesting for traditional medicine, pet trade, and food, it is critical to assess their conservation status.
The publication was based on the bachelor thesis of Lilli Stenger conducted at the University of Cologne, Germany. “Being able to focus my bachelor thesis on the threat status of the reptiles extant in Vietnam was a great opportunity and I am proud of this contribution,” says Lilli Stenger about her thesis project performed in Ziegler’s lab at the Cologne Zoo, Germany.
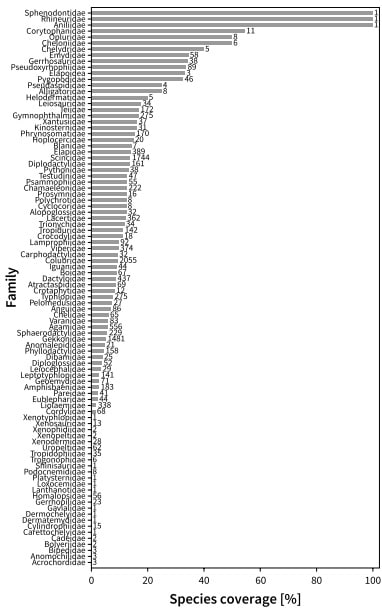
The scientists identified 484 reptile species known from Vietnam, noting that the number is likely to go up, as the country is regarded as a top biodiversity hotspot, and the rate of new reptile species discoveries remains high. As many as 159 (33%) reptile species are endemic to the country, with more than half of them (55%) reported exclusively from only a single locality, making them especially vulnerable to extinction.
“With 131 subregional endemic species and 88 of them restricted to their type locality, the country needs to establish additional local conservation areas to safeguard the microendemic species.” explains one of the authors of the present study, Prof. Dr. Truong Quang Nguyen of the Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources (IEBR), Hanoi.
According to the IUCN Red List of threatened species, 74 of the 484 species recorded from Vietnam are classified as threatened with extinction, including 34 endemic species. Most of threatened reptiles are lizards, followed by snakes and turtles, with 100% of the species in Vietnam listed as Vulnerable or higher. For more than half of Vietnam’s endemic reptiles (85 out of 159), the IUCN Red List status is either missing or outdated and further research is imperative for these species, the researchers say.
According to species richness maps, the Central Annamites region in central Vietnam harbors the highest endemic species diversity (32 species) as well as highest subregional endemic species diversity (21 species), which highlights it as a site of particular importance for reptile conservation.
“Integrating microhabitat level species richness maps and spatial patterns of local endemism rates is essential to identify priority areas for further conservation measures as habitat loss and increased anthropogenic pressures in these areas would adversely affect a higher number of species than it would in other areas” explains Associate Professor Dr. Dennis Rödder, curator of herpetology of the Leibniz Institute for the Analysis of Biodiversity Change, Museum Koenig in Bonn, Germany.
Alarmingly, a protected area analysis showed that 53 of the 159 endemic species (33.2%) including 17 threatened species, have been recorded exclusively from unprotected areas, such as the Critically Endangered Gia Lai Bent-toed Gecko or Endangered Peter’s Butterfly Lizard and Psychedelic Rock Gecko.
“For these species as well as for the 28 species considered Data Deficient (DD) or those whose conservation statuses have not been evaluated (NE), population assessments should be undertaken as quickly as possible to design appropriate conservation measures in due time,” says co-author Dr. Cuong The Pham from IEBR.
Successful protection must also include the listing of the most threatened endemic species in national and international legislations to provide them with additional support, as many threatened and/or endemic species are still missing from those legislations. The Vietnamese-German team already could achieve first promising results such as the inclusion of some threatened Vietnamese lizard species in the appendices of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), but more of such advances are still needed.
According to data from Species360’s Zoological Information Management System (ZIMS), 109 (22.5%) of the total 484 species reported to occur in Vietnam are represented in global zoos, with the highest diversity concentrated in facilities in Europe and North America. However, only 6.3% (10 out of 159) of the Vietnamese endemic species are maintained ex situ, thus it is crucial that zoos consider shifting their focus to commit more resources to threatened endemic species.
In order to successfully protect threatened species and meet the objectives of the One Plan Approach of IUCN’s Conservation Planning Specialist Group (CPSG), which refers to the interaction of “in situ” (on site) and “ex situ” (in zoos and stations) measures involving various expertise and thus enabling optimized, contemporary species conservation, ex situ populations must be included in global conservation planning. “This is intended to support the in situ conservation efforts and to buy time as well as to save species from going extinct, as ex situ populations still are available for reintroductions” says co-author Anna Rauhaus, section keeper in Cologne Zoo’s Terrarium division, where 36 species of herpetofauna from Vietnam are held, 19 of them threatened and 25 species of them successfully bred, and most of them connected with in situ conservation measures in Vietnam. .
“Two most endangered turtle species in Vietnam and in the world, the Vietnamese pond turtle (Mauremys annamensis) and the Yangtze giant softshell turtle (Rafetus swinhoei), illustrate the significance of ex situ conservation measures. Both of the species are also not known from any protected area. While Mauremys annamensis is likely to be extinct in the wild, Rafetus swinhoei is on the brink of extinction. Whereas ex situ conservation programs have been implemented in time for Mauremys annamensis with a high number of individuals being kept and bred in zoos and stations, unfortunately, no such initiative has been established for Rafetus swinhoei”, Prof. Dr. Minh Le from the Hanoi National University emphasizes.
“In this regard, modern zoos, as well as local facilities, can play a crucial role in not only conducting or financially supporting in situ conservation projects, but also by protecting species from extinction through maintaining ex situ assurance colonies to reinforce in situ conservation programs, once needed. The Cologne Zoo in Germany and its partner, the Melinh Biodiversity Station in Vietnam, have already successfully implemented a number of conservation breeding initiatives for highly threatened species such as Vietnamese crocodile lizards or Tiger geckos “ explains Prof. Dr. Thomas Ziegler, Vietnam conservation team member and coordinator from Cologne Zoo, Germany.
The present study aims to provide a baseline to authorities, conservationists, rescue centers, and zoos, so that they can follow up with appropriate conservation measures for endangered Vietnamese reptiles.
ICVM 2023, Cairns, Australia
My PostDoc Dr. Jendrian Riedel joint the 13th International Congress of Vertebrate Morphology in Cairns, Australia, presenting our results on gecko morphology. The conference was a great opportunity to meet vertebrate morphologists from across the globe, with many fantastic presentations spanning a wide range of organisms, methods, and research questions.
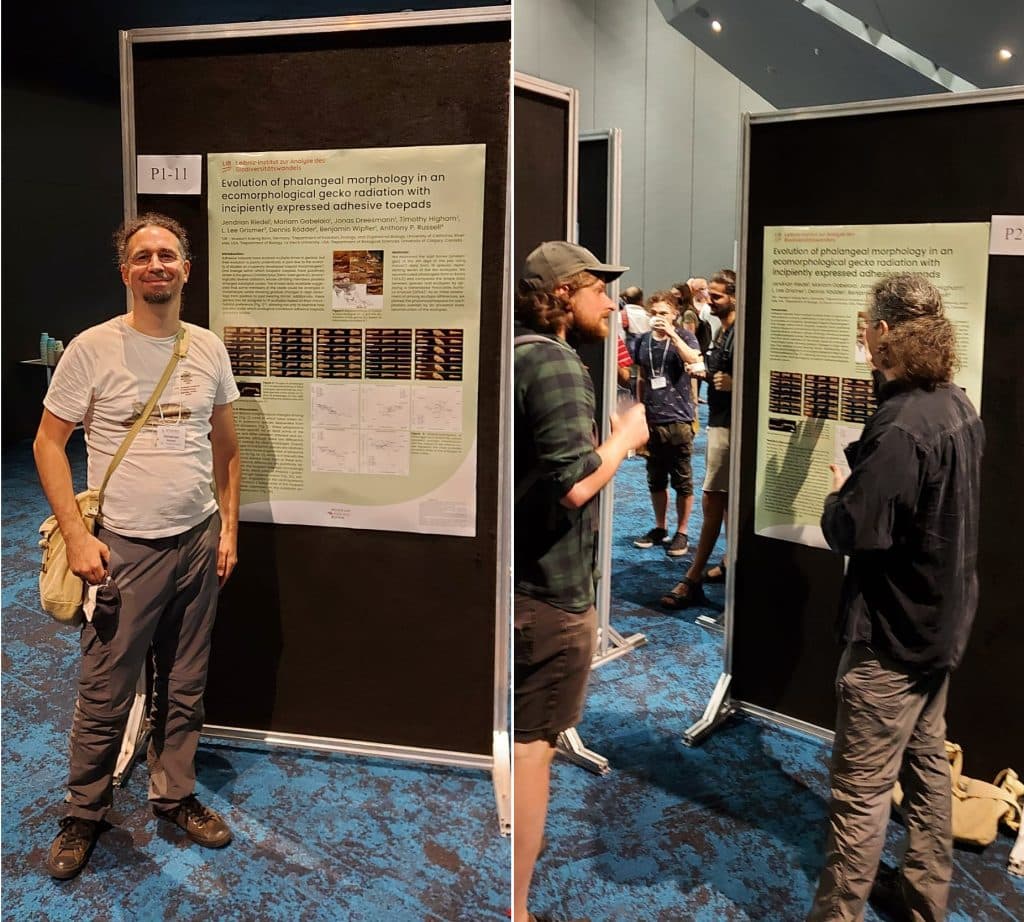

Evolution of phalangeal morphology in an ecomorphological gecko radiation with incipiently expressed adhesive toepads
Jendrian Riedel, Mariam Gabelaia, Jonas Dreesmann, Jannis Manno, Timothy Higham, L. Lee Grismer, Dennis Rödder, Benjamin Wipfler, Anthony P. Russell
Adhesive toepads, complex morphological structures enabling animals to exhibit astonishing climbing abilities, have evolved multiple times in geckos. Although well studied in a few exemplar clades in terms of function and morphology, their evolution is poorly understood, in part due to the scarcity of studies on incipiently developed toepad morphologies. One lineage within which incipient toepads has been suggested to have arisen is the genus Cyrtodactylus (bent-toed geckos), an ecologically diverse radiation, whose climbing members possess enlarged subdigital scales. The limited data available suggested that some members of the clade could be arranged in morphotypic series showing gradual changes in digit osteology from padless to pad bearing forms. With the phylogeny of the genus now much better resolved and knowledge about their microhabitat use greatly enhanced, we are now able to conduct a phylogenetically informed investigation of digit osteology using microCT data and applying 3D geometric morphometrics. We explored whether, and if so how, repeated gradual changes in digit osteology have occurred in scansorial species and whether such modifications differ depending on the locomotor substrate (e.g., arboreal vs. saxicolous species). We found that distinct morphological changes have arisen repeatedly in scansorial species descending from generalist ancestors. These adaptations are substrate specific for at least some of the phalanges, differing between arboreal and saxicolous species, although there were differential degrees of overlap in other phalanges.
A global analysis of habitat fragmentation research in reptiles and amphibians: what have we done so far?
Our new review on habitat fragmentation research in amphibians and reptiles is just published in Biodiversity and Conservation early online! My PhD student Nicholas Tan did a great job analysing the global patterns of research agendas based on more than 1400 papers, comparing methodological and taxonomic biases across geographical regions. The full text is available here:
Habitat change and fragmentation are the primary causes of biodiversity loss worldwide. Recent decades have seen a surge of funding, published papers and citations in the field as these threats to biodiversity continue to rise. However, how research directions and agenda are evolving in this field remains poorly understood. In this study, we examined the current state of research on habitat fragmentation (due to agriculture, logging, fragmentation, urbanisation and roads) pertaining to two of the most threatened vertebrate groups, reptiles and amphibians. We did so by conducting a global scale review of geographical and taxonomical trends on the habitat fragmentation types, associated sampling methods and response variables. Our analyses revealed a number of biases with existing research efforts being focused on three continents (e.g., North America, Europe and Australia) and a surplus of studies measuring species richness and abundance. However, we saw a shift in research agenda towards studies utilising technological advancements including genetic and spatial data analyses. Our findings suggest important associations between sampling methods and prevalent response variables but not with the types of habitat fragmentation. These research agendas are found homogeneously distributed across all continents. Increased research investment with appropriate sampling techniques is crucial in biodiversity hotpots such as the tropics where unprecedented threats to herpetofauna exist.


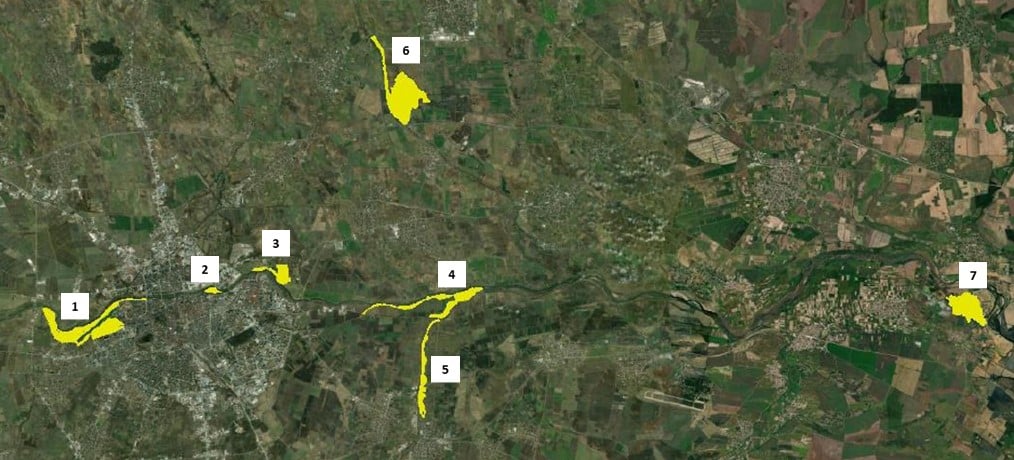
Spatiotemporal habitat use and impacts of habitat fragmentation on Lizards
My group just published two new papers on the effects of habitat loss on tick load in the eastern green lizard Lacerta viridis and spatiotemporal patterns of habitat use by the sand lizard Lacerta agilis. Both studies required numerous hours of fieldwork and many students were involved. Special thanks to all of them for their enthusiasm!
The distribution and occurrence of a species in its habitat are inevitably linked to its ecology. To successfully monitor and protect species, it is important to investigate which species-specific factors influence its interactions with the environment. In this study, we focus on patterns in habitat use of the Sand Lizard (Lacerta agilis). Differences in seasonal, as well as sex and size class-dependent habitat use, have been reported from the edges of this species’ range. To verify such trends in the core area of its distribution, we analyzed the habitat factors weather, microclimate, microhabitat structures, and time dependence, which may have an impact on the use of space of the Sand Lizard. Using generalized linear models, hypervolumes, density estimations, and Chi-squared tests, we found that the movement patterns of individuals can neither be described by time differences, climatic conditions, or habitat composition nor do they show habitat- or weather-related differences of movement between sexes or size. Here we demonstrate that in the case of a population from the core of this species’ distribution area in the Dellbrücker Heide (Germany), habitat use is solely influenced to a low degree by differences related to the ontogeny of Sand Lizards and does not depend on any of the other evaluated factors. These results are in enormous contrast to findings in populations from the periphery of their distribution, i.e., the United Kingdom, Latvia, Romania, Bulgaria, and the Pyrenees. This implies that seasonal habitat shifts are more extreme at the edges of the range of L. agilis, serving to compensate deteriorating habitat conditions in the periphery.

Habitat loss can increase the susceptibility of individuals to parasitic infections, and hence, parasite load can serve as an early warning indicator of stress before the persistence of a population becomes threatened. In this study, we tested the effects of patch characteristics, isolation and landscape composition resulting from habitat loss on the tick load of individuals from central populations of the Eastern Green Lizard Lacerta viridis. We identified the spatial scale at which each landscape composition parameter has the strongest effect and evaluated its effects at this scale. Additionally, we tested the relationships between tick load and population density and body condition (BC) to understand possible mechanisms that determine tick loads in populations. We found that tick load was not affected by host population density. BC was not found to be affected by tick load, but BC did have a negative effect on lizards’ tick loads. The proportion of habitat and cropland in the landscape and patch size had positive effects on tick loads, whereas the proportion of urbanized areas, isolation and perimeter/area ratio had negative effects. We discuss our finding in the context of how the landscape can affect tick populations and other potential hosts. We conclude that tick load can be a suitable early warning indicator of negative effects of habitat loss, reflecting the susceptibility of lizards to infestation. We suggest that this indicator be included in monitoring programs aiming at evaluating the status of populations of L. viridis in modified landscapes, and recommend that conservation measures be focused on the protection of habitat at broader scales to compensate negative effects of cropland and urbanized areas occurring at small scales.